How does it work?
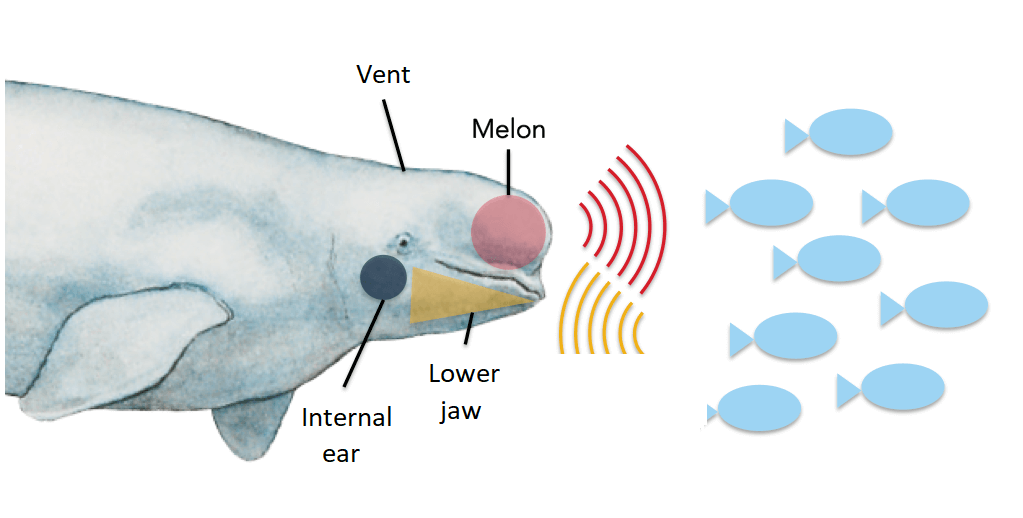
Echolocation takes place in two stages: first, the animal emits sounds and then it analyzes them. The sounds originate in the whale’s head and are concentrated in the melon, the bulge on its forehead.
When the sound strikes an object, it returns to the animal through sound-conducting tissue in the lower jaw. From there, it travels to the inner ear (whales have no external ear!), where it completes its journey. The brain then processes the information.
Last updated: July 2019